As fast and wide as the PCI bus was, there was one task that threatened to consume all its bandwidth: displaying graphics. Early in the era of the ISA bus, monitors were driven by simple Monochrome Display adapter (MDA) and Colour Graphics Array (CGA) cards. A CGA graphics display could show four colours (two bits of data) at 320 by 200 pixels screen resolution at 60Hz, which required 128,000 bits of data per screen, or just over 937 KBps. An XGA image at a 16-bit colour depth requires 1.5MB of data for every image, and at a vertical refresh rate of 75Hz, this amount of data is required 75 times each second. Thanks to modern graphics adapters, not all of this data has to be transferred across the expansion bus, but 3D imaging technology created new problems.
AGP Pro is a physical specification aimed at satisfying the needs of high-end graphics card manufacturers, who are currently limited by the maximum electrical power that can be drawn by an AGP card (about 25W). AGP Pro caters for cards that draw up to 100W, and will use a slightly longer AGP slot that will also take current AGP cards. For instance, your PC consists of a monitor which is attached to your CPU with the help of a graphics card and this is where the use of a PCI comes. All these types of external devices can be connected to the PCI slot, a plug, and play system in your PC scans and recognize the device attached to the PCI slot and there you go on with your favorite movie on your computer screen. There have been a number of benchmarks (google them or ask a friend with AGP to bench) showing that the difference between running an AGP card at 8x and 4x is negligible. Thats why many people were upset when the switch to PCI-E occured because it was obvious that the full eight lanes of AGP weren't saturated.
3D graphics have made it possible to model both fantastic and realistic worlds on-screen in enormous detail. Texture mapping and object hiding require huge amounts of data, and the graphics adapter needs to have fast access to this data to avoid the
AGP operates at the speed of the processor bus, now known as the frontside bus. At a clock rate of 66MHz this is double the PCI clock speed and means that the peak base throughput is 264 MBps.
For graphics cards specifically designed to support it, AGP allows data to be sent during both the up and down clock cycle, doubling the clock rate to 133MHz and peak transfer to 528 MBps. This is known as 2x. To improve the length of time that AGP can maintain this peak transfer, the bus supports pipelining, which is another improvement over PCI. A pipelining 2x graphics card will be able to sustain throughput at 80% of the peak. AGP also supports queuing of up to 32 commands via a process called Sideband Addressing (SBA), the commands being sent while data is being received. This allows the bus to sustain peak performance for 95% of the time, according to Intel.
Agp Slot Full Form Code

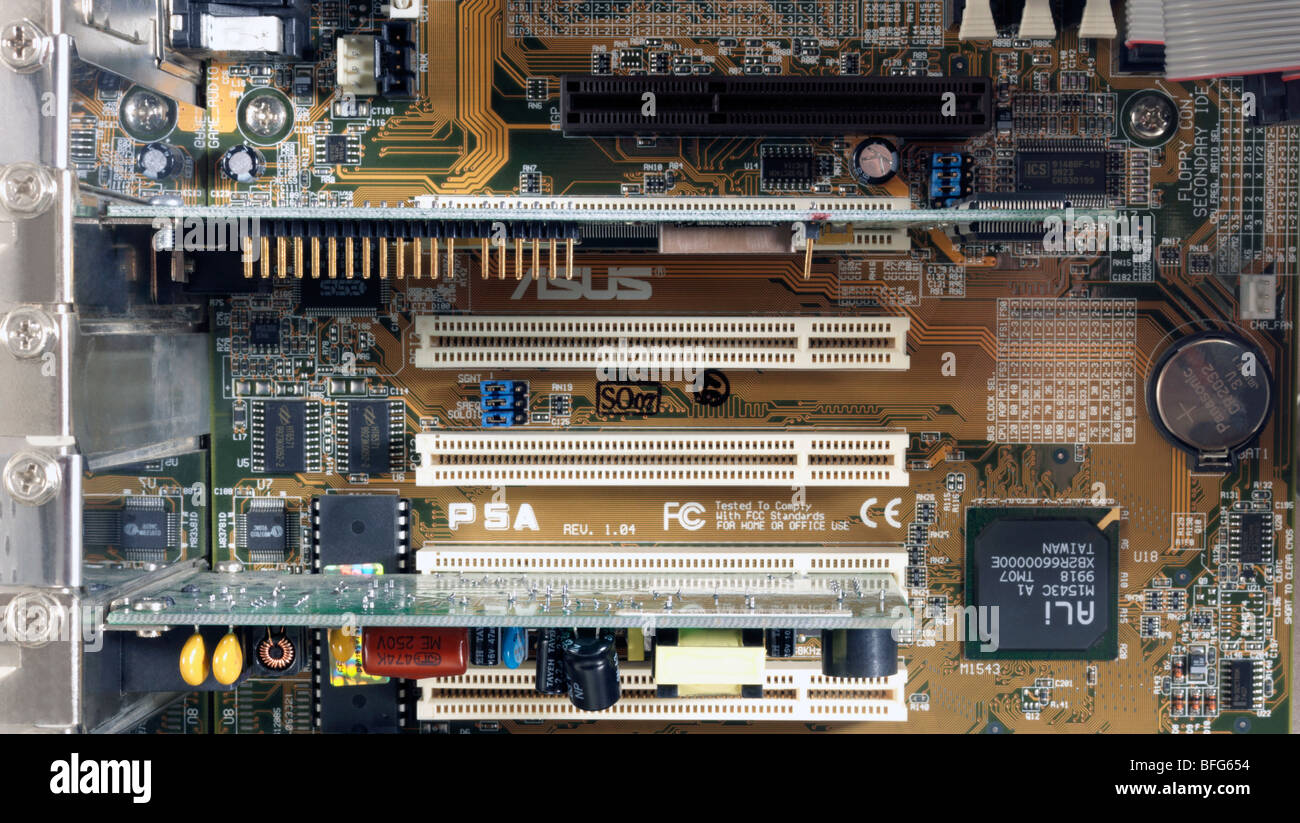
AGP’s four-fold bandwidth improvement and graphics-only nature ensures that large transfers of 3D graphics data don’t slow up the action on screen; nor will graphics data transfers be interrupted by other PCI devices. Being primarily intended to boost 3D performance, AGP also provides other improvements that are specifically aimed at this function.
Agp Slot Full Form Download
With its increased access speed to system memory over the PCI bus, AGP can use system memory as if it’s actually on the graphics card. This is called Direct Memory Execute (DIME). A device called a Graphics Aperture Remapping Table (GART) handles the RAM addresses so that they can be distributed in small chunks throughout system memory rather than hijacking one large section, and presents them to a DIME-enabled graphics card as if they’re part of on-board memory. The main use for DIME is to allow much larger textures to be used because the graphics card can have a much larger memory space in which to load the DRDRAM) in the second half of 1999. AGP 2.0 was supported by chipsets launched early in 1999 to provide support for Intel’s Katmai processor.
AGP Pro is a physical specification aimed at satisfying the needs of high-end graphics card manufacturers, who are currently limited by the maximum electrical power that can be drawn by an AGP card (about 25W). AGP Pro caters for cards that draw up to 100W, and will use a slightly longer AGP slot that will also take current AGP cards.
The motherboard features a 4+1 phase CPU power circuit. It features two PCI-Express 2.0 x16 slots for ATI CrossFire, and a PCI-Express x4 slot. Sadly it lacks PCI slots. It has six DDR3 DIMM slots for DDR3-1333 MHz memory. It features six SATA II ports, 7.1ch HD audio among other standard features.
23 Commentson Gateway TBGM-01 MATX X58 Motherboard Pictured

Agp Slot Full Form Definition
#1Agp Slot Full Form Medical
